
Test analysts will engage with business and operational stakeholders, providing a forward view of demand.
#SECURITY SHIFT LEFT SOFTWARE#
There are some key strategies that will help you shift left with your software testing: Demand planning Collaborate with customers to determine what is working (instead of working from assumptions)Ĭontinuous feedback from users may help in responding better to software failures.Validate a hypothesis by trying out new solutions.Reviews and feedbacks from targeted users further help in enhancing the quality of the software.Īn important characteristic of the Shift Right approach is a willingness to: In this Shift Right practice, you’ll test a completely built and functioning application to ensure performance and usability traits. Shift Right initiates testing from the right, i.e., post-production.


Research from the Ponemon Institute, in 2017, found that if vulnerabilities get detected in the early development process, they may cost around $80 on an average. The cost of resolving these defects works in reverse:Ī defect that is removed after the product has gone into product will cost around 100 times more than one that is identified and removed during the requirements phase. Estimates indicate that over half of all software defects could be identified during the requirements phase, with less than 10% emerging during the development phase of the lifecycle. The problem is that these practices can’t handle changing expectations and requirements, resulting in negative outcomes for the business such as:Ĭost alone is a very strong incentive for shifting your testing to the left.

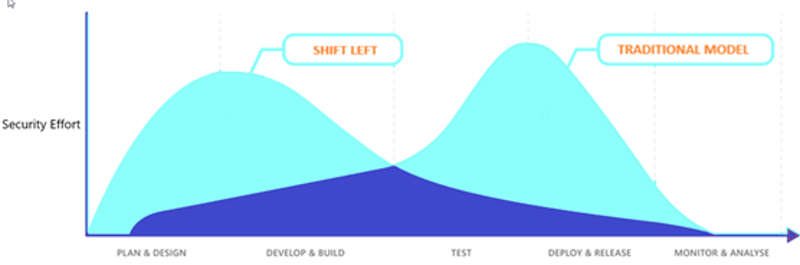
In the traditional software development model, requirements are kept on the left side of the plan, and the delivery and testing requirements on the right. Shift Left testing means testing earlier in the software development process. The idea is to improve quality by moving tasks to the left as early in the lifecycle as possible. Shift Left is a practice intended to find and prevent defects early in the software delivery process. Recognizing the bottleneck here, we now want to move the initiation of testing as far to the left as possible. In the old model, testing only came into play on the far right of the line. The easiest way to explain shift-left software testing is to think of the development cycle as a line running from left to right. In this model, testing became a bottleneck that seriously impeded the ability of projects to deliver on time. This meant that when bugs or usability issues were inevitably found, the release would be delayed until these were fixed. Traditional testingĪ typical waterfall software development project would have seen testing occur immediately prior to release into production. Bringing development and testing together early is commonly referred to as ‘shifting left’.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
